
In today’s fast-paced learning environment, students need more than natural skills and hard work to succeed. One of the most critical skills for academic achievement is self-management—the ability to regulate thoughts, emotions, and actions to reach goals efficiently.
But success isn’t a one-size-fits-all concept. Every student has different strengths, challenges, and levels of support. Understanding how self-management skills impact academic performance can help students, parents, and educators create strategies that foster independent learning and long-term success.
What Are Self-Management Skills?
Self-management skills encompass a set of mental abilities that help students:





These skills play a significant role in determining how students handle schoolwork, responsibilities, and personal growth. The more refined a student’s self-management abilities, the more independent and successful they become.
Why Self-Management is Key to Success
Students with strong self-management skills can:




On the other hand, students who struggle in these areas may face academic difficulties and require additional support from parents, teachers, or mentors.
Different Paths to Success: Understanding the Balance
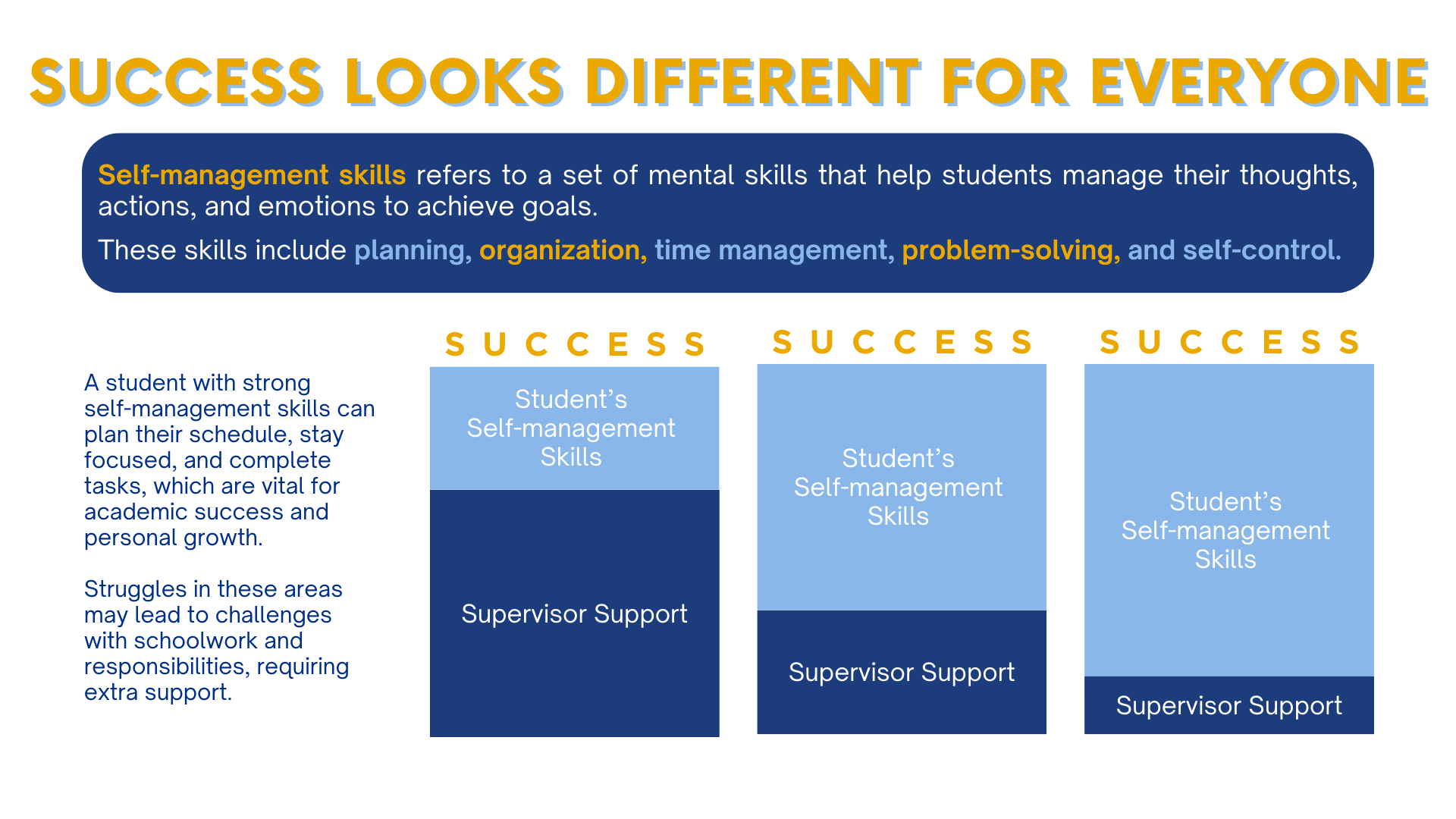
The slide highlights an essential truth: success looks different for everyone. Some students naturally excel at self-management, while others may need more external guidance to thrive.
The diagram above presents three variations of success:
1. High Self-Management Skills, Minimal Support Needed
Students in this category are independent learners who:




These students need minimal external supervision because they have developed a strong sense of responsibility and discipline.
2. Moderate Self-Management Skills, Some Support Required
These students can manage most of their tasks but still benefit from occasional supervisor support. They may:



With the right guidance, these students can gradually improve their self-management skills and move toward greater independence.
3. Low Self-Management Skills, High Support Needed
Some students require significant supervision to stay organized and productive. They may:




For these students, parental and educator involvement is crucial. Using structured learning strategies, positive reinforcement, and organizational tools can help them build better habits.
How to Strengthen Self-Management Skills
Whether a student is naturally organized or needs extra support, these strategies can help them develop stronger self-management habits:
1. Teach Effective Planning



2. Build Time Management Skills



3. Encourage Problem-Solving and Critical Thinking



4. Provide the Right Level of Support



The Role of Parents and Educators in Student Success
As highlighted in the slide, supervisor support varies depending on a student’s self-management abilities. Supervisors play a crucial role in helping students build these skills at a pace that suits their learning style.
Some ways to provide effective support include:




The ultimate goal is to help students become independent, responsible learners who take charge of their education and future success.
Final Thoughts
Success in academics and beyond is deeply tied to self-management skills. While some students naturally excel in organization, time management, and problem-solving, others may need additional guidance to develop these skills.
At NorthStar Academy, we believe that every student’s path to success is unique. By understanding and nurturing self-management, students can unlock their full potential and thrive in any learning environment. If you’re looking for an education platform that supports student growth, independence, and self-management, NorthStar Academy is here to help. Contact us today to learn more about how we empower students for success!
